Distributed Lock Manager笔记
[toc]
本文源自对陈皓老师Distributed Lock Manager的分享。
Consistency
比如对于一个订单,买家取消订单、商家发货这两个动作,先后顺序不一样,走的流程也不一致。
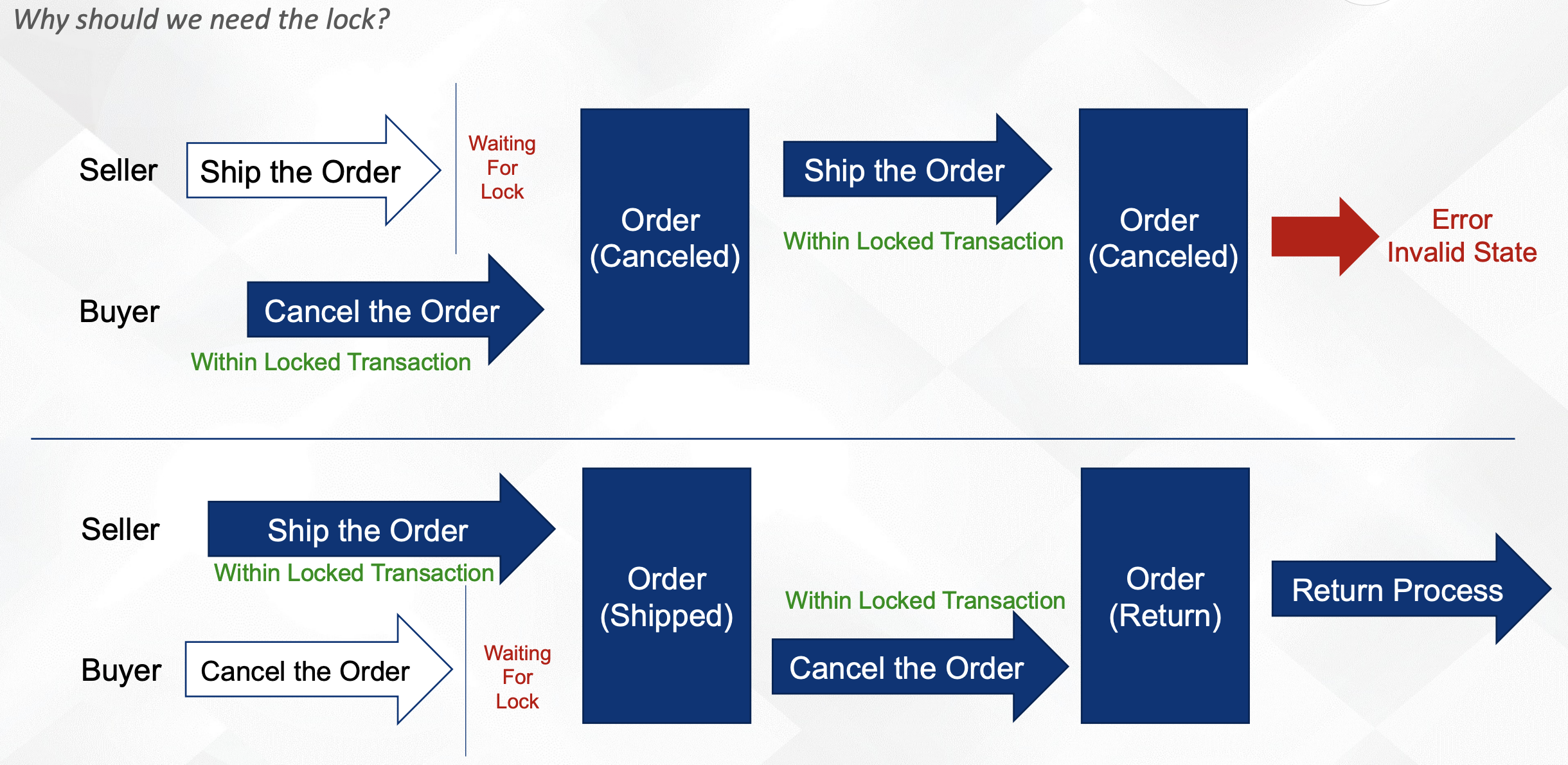
锁的类型
- 数据库锁(Database Lock)
- 应用Sharding(Shard Application)
- 中心分布式锁(Centralized Distributed Lock Manager)
DB Lock
以MySQL InnoDB Lock举例:
共享锁(Shared Lock)
含义:我在写,别人可以读
1 | SELECT * LOCK IN SHARED MODE |
排他锁(Exclusive Lock)
含义: 我在写,别人不可以读。
可能存在的坑:与Where条件强相关,如果where的结果是一个范围,可能会导致插入时也会失败,比如where id >= $ID,当插入数据时,如果ID是自增的,此时插入不进去,因为此时ID在被锁的范围内。
1 | SELECT ... FOR UPDATE |
上面两种锁都是悲观锁,可能会导致死锁:跟锁的顺序有关,使用时一定要注意。
乐观锁(Versioning Optimistic Lock)
1 | -- 1. |
乐观锁性能高,但是失败时可能需要不停访问数据库。
Shard模式
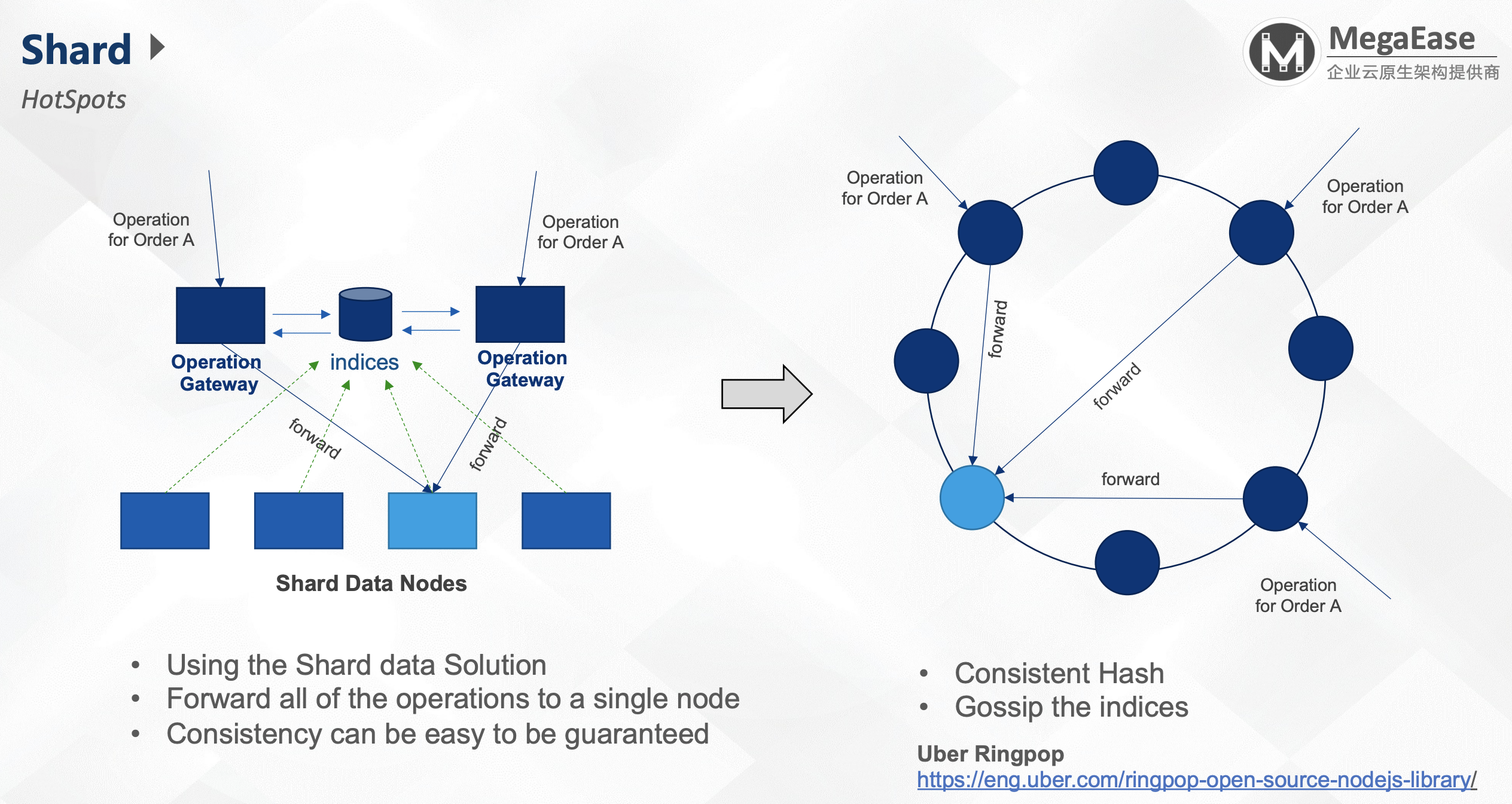
流程:
- 将数据分片到不同的节点。
- 数据的索引交给索引服务器(indices),索引服务器前面是两个Gateway。
- Gateway通过数据发现,对数据(Order A)全部转向同一个节点上。
- 对同一个节点上的数据,可以使用多线程的一些方法(比如Mutex)来锁处理数据。
当前方法的问题:
- 存在热点数据
- 扩节点时需要reshard所有数据
由此,我们使用一致性哈希(Consistent Hash)。
Uber Ringpop:通过gossip方式进行数据同步,但是当前Uber已经放弃了。https://eng.uber.com/ringpop-open-source-nodejs-library/
Shard问题:
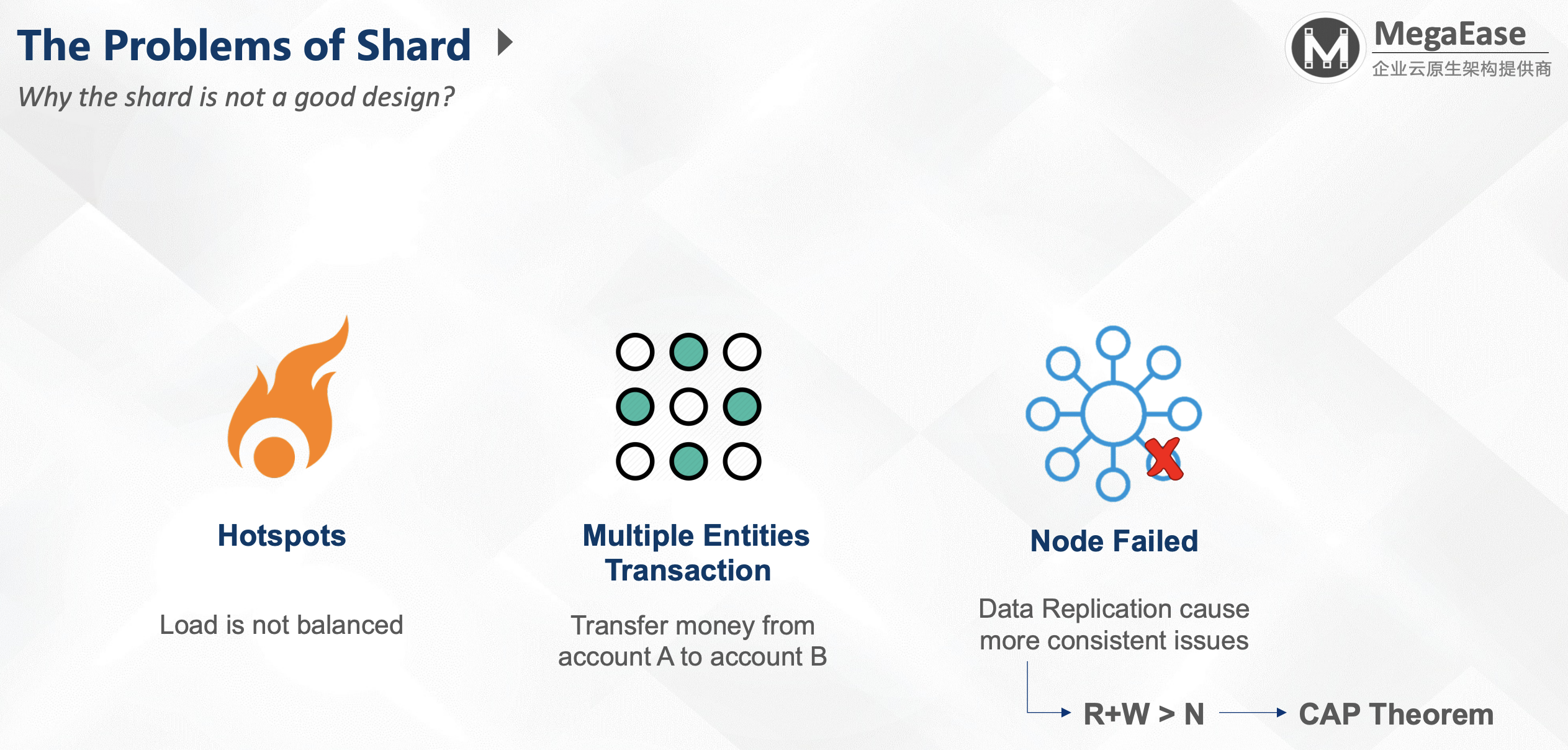
- 热点数据
- 多个数据的问题(Multiple Entities Transaction): 比如从A账户转账到B账户
- 节点失效时的数据复制倒置的一致性问题:R+W>N –> CAP理论 (NRW: 读的节点与写的节点大于N节点:写过半时是强一致性的,如果写未过半,此时是AP系统,需要自己Merge)
Distributed Lock Manager
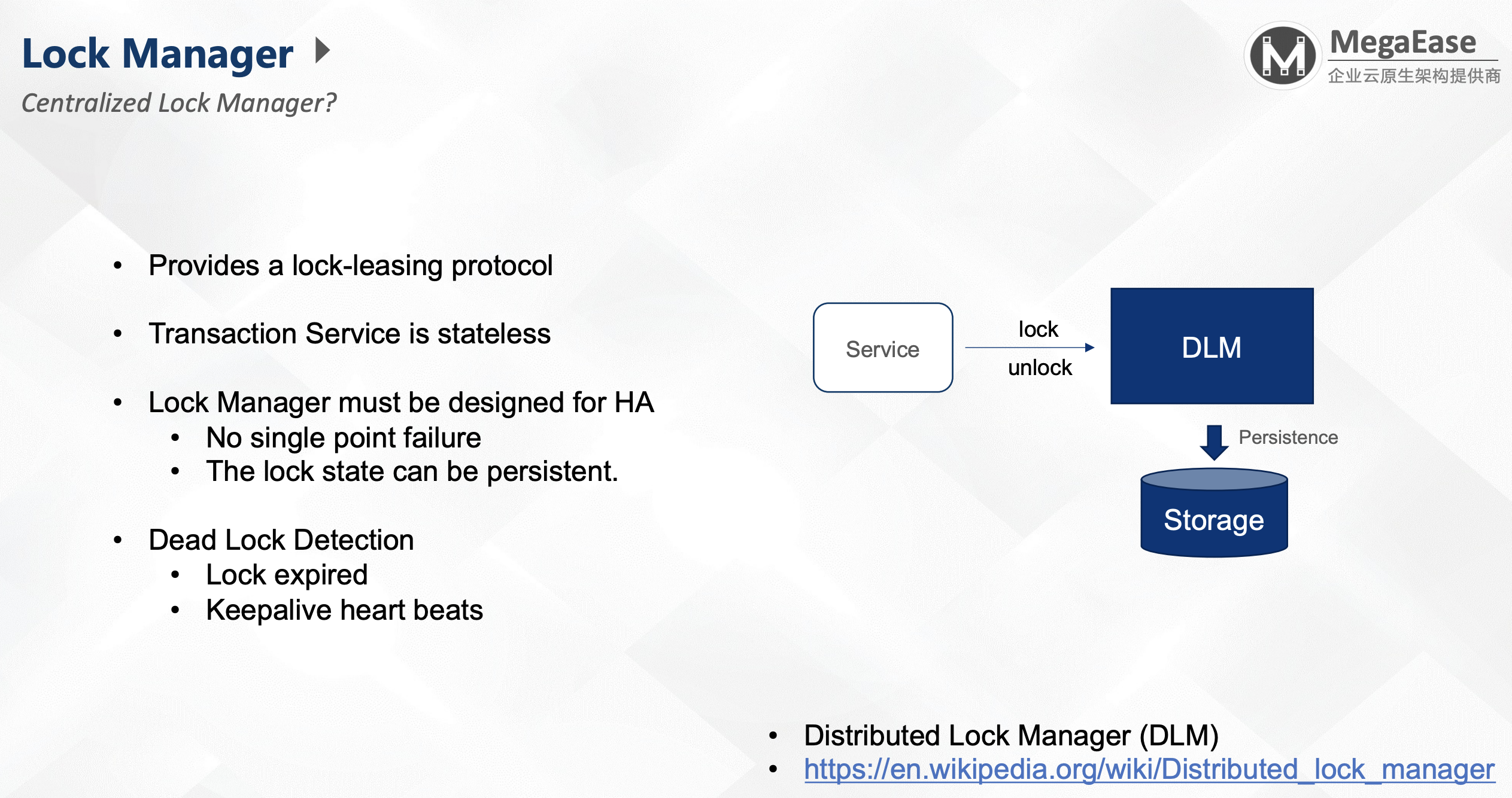
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Distributed_lock_manager
DLM:分布式锁管理器,由他统一管理锁。需要注意的是,DLM一定要能对锁进行持久化,否则容易造成数据丢失。
- 要提供锁的租约机制:防止加锁后,持有锁的对象不释放锁。
- Lock Manager需要高可用,没有单点故障,锁状态可持久化。
- 死锁检测:
- 锁过期(Lock expired)
- 保活心跳(Keepalive heart beats)
DLM Lock Modes
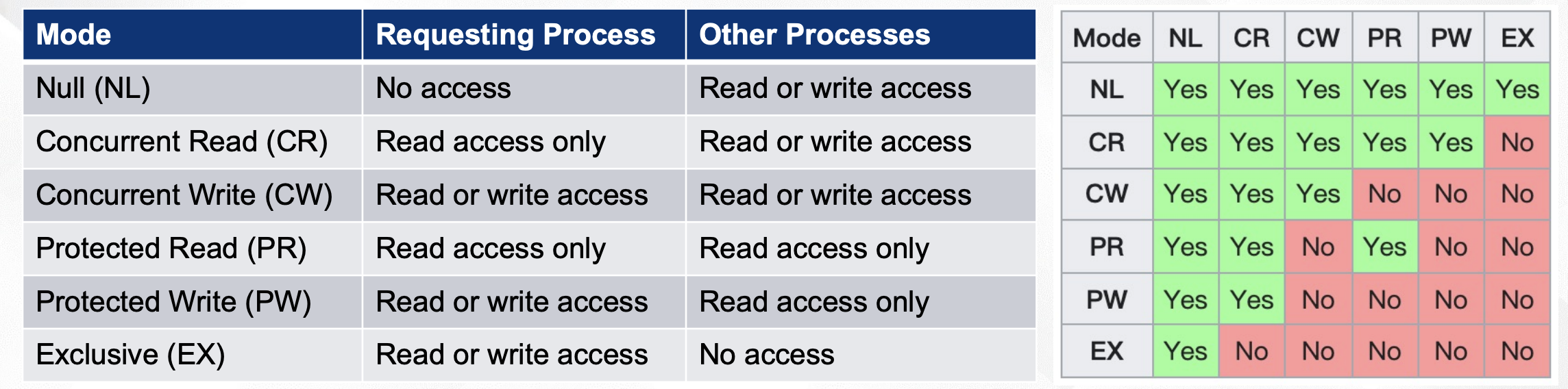
上面是Wikipedia中的6种锁模型:
- 无锁
- 并发读
- 并发写
- 保护读
- 保护写
- 排他锁
前三个没什么,主要是后面三个。
Redlock
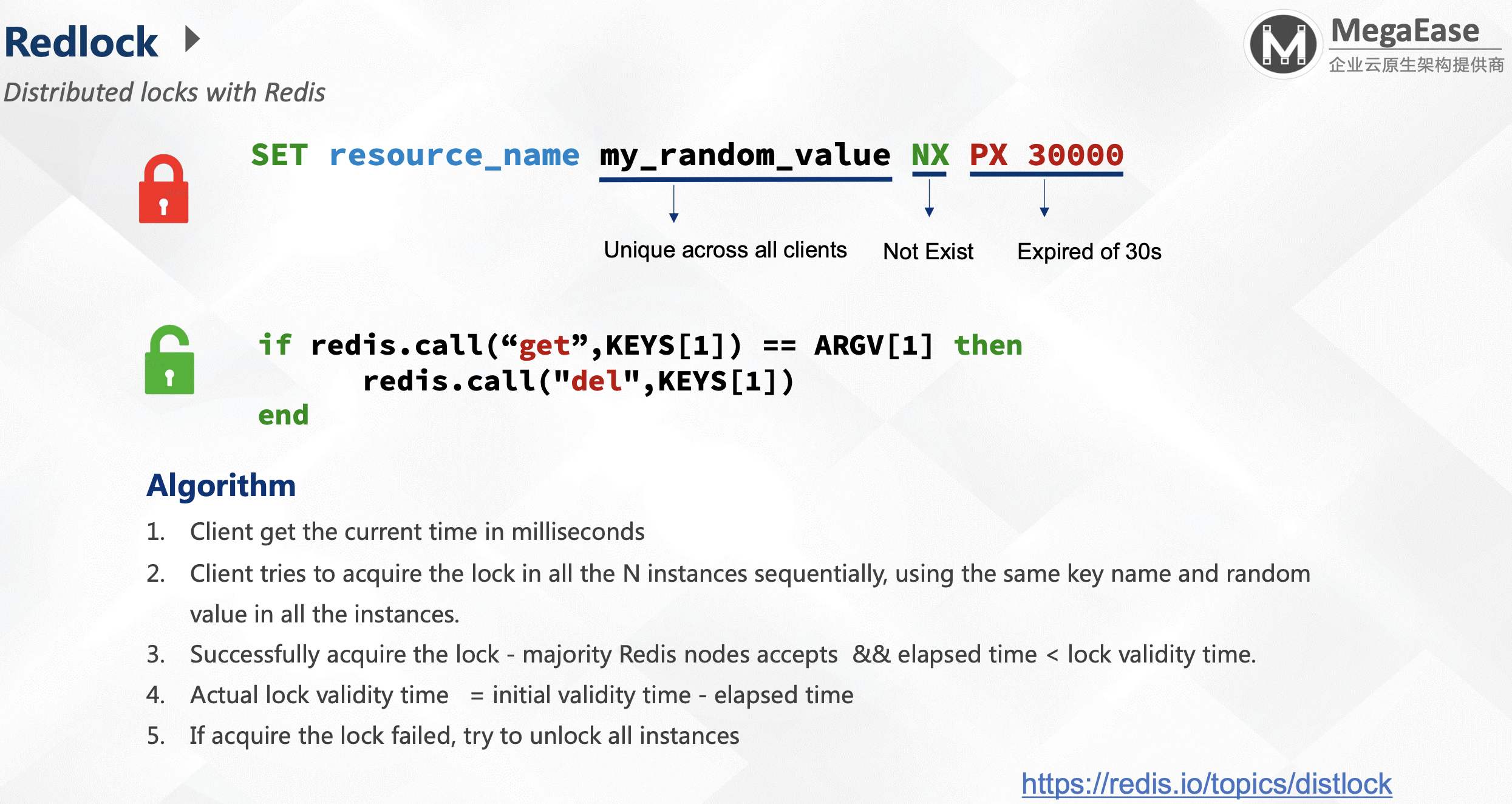
https://redis.io/topics/distlock
算法:
- 客户端获取当前时间(精确到毫秒);
- 客户端按照顺序请求N个实例的锁。对这N个实例上锁时使用相同的key名称与随机值,随机值需要是唯一的;
- 当获得的锁节点的数量大于半数,且消耗的时间(elapsed time) < 锁有效的时间(lock validity time);
- 锁实际有效时间=初始有效时间 - 消耗时间(Actual lock validity time = initial validity time - elapsed time):这是为了让锁同时失效,而不是参差不齐的时间点失效;
- 如果获取锁失败了,尝试释放掉所有实例。

这个存在一些问题:
- 时间跳变导致的锁失效;
- 如果client 1获取C节点后hang住,在锁失效后又恢复了;
- client 1 与节点C之间通信有很大的网络延迟。
Martin Kleppmann(写DDIA的老哥) 提出上面的挑战后,给了一个非常著名的结论:
the algorithm makes dangerous assumptions about timing and system clocks(算法依据时间和系统时钟不靠谱)
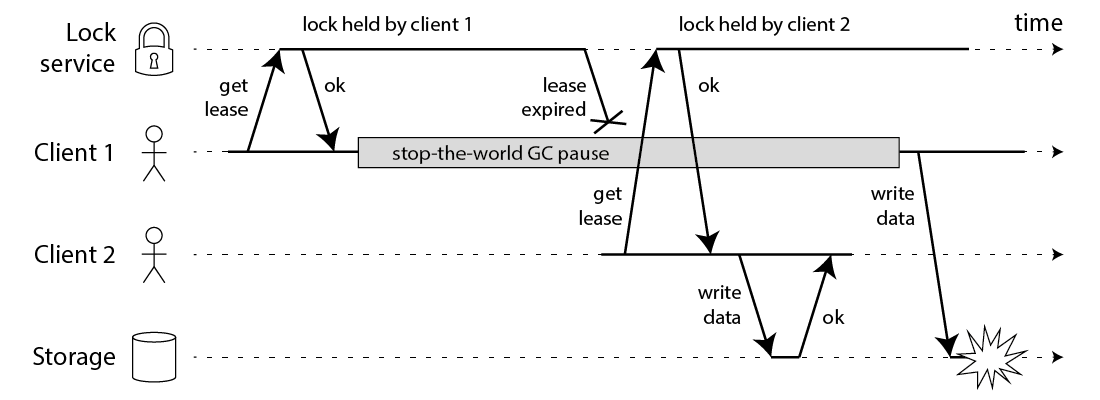
于是老哥就给出了一个如何做分布式锁的文章:How to do distributed locking.
老哥给出了使用fencing token的方案:
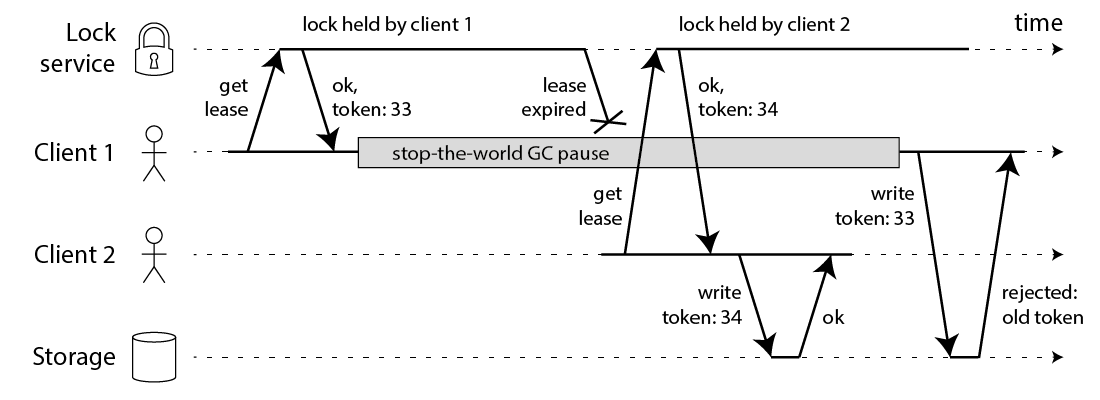
该方案需要锁服务与数据配合,锁服务提供token,数据对token进行单调性验证。本质上是一个乐观锁,而且需要数据存储侧配合,比较复杂。
于是Redis作者Antirez做出了回应:
TL;DR http://antirez.com/news/101
- 用这个方案还要分布式锁干啥,直接用乐观锁不就行了(Fencing is great, with this, no need distributed lock!)
- 时钟跳变是个大问题,Redlock搞不定(Clock jump is a big problem, Redlock cannot work correctly)
under this problem. - Redlock能搞定网络延时和hang住的问题(For network delay & client hangs, they all will be fine.)
Antirez最后说,分布式锁做的最好的是Zookeeper。
Zookeeper
https://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/r3.1.2/recipes.html
上面的连接给了几个比较厉害的Zookeeper用法,包含了分布式锁。
- 在
_locknode/lock-下创建顺序临时节点(Create_locknode/lock-with Sequence & Ephemeral flag) - 这些节点看是不是节点下最小的(Get children to see to check if I am the lowest sequence number)
- Yes. Get the Lock
- No. Set the watch

Google Chubby
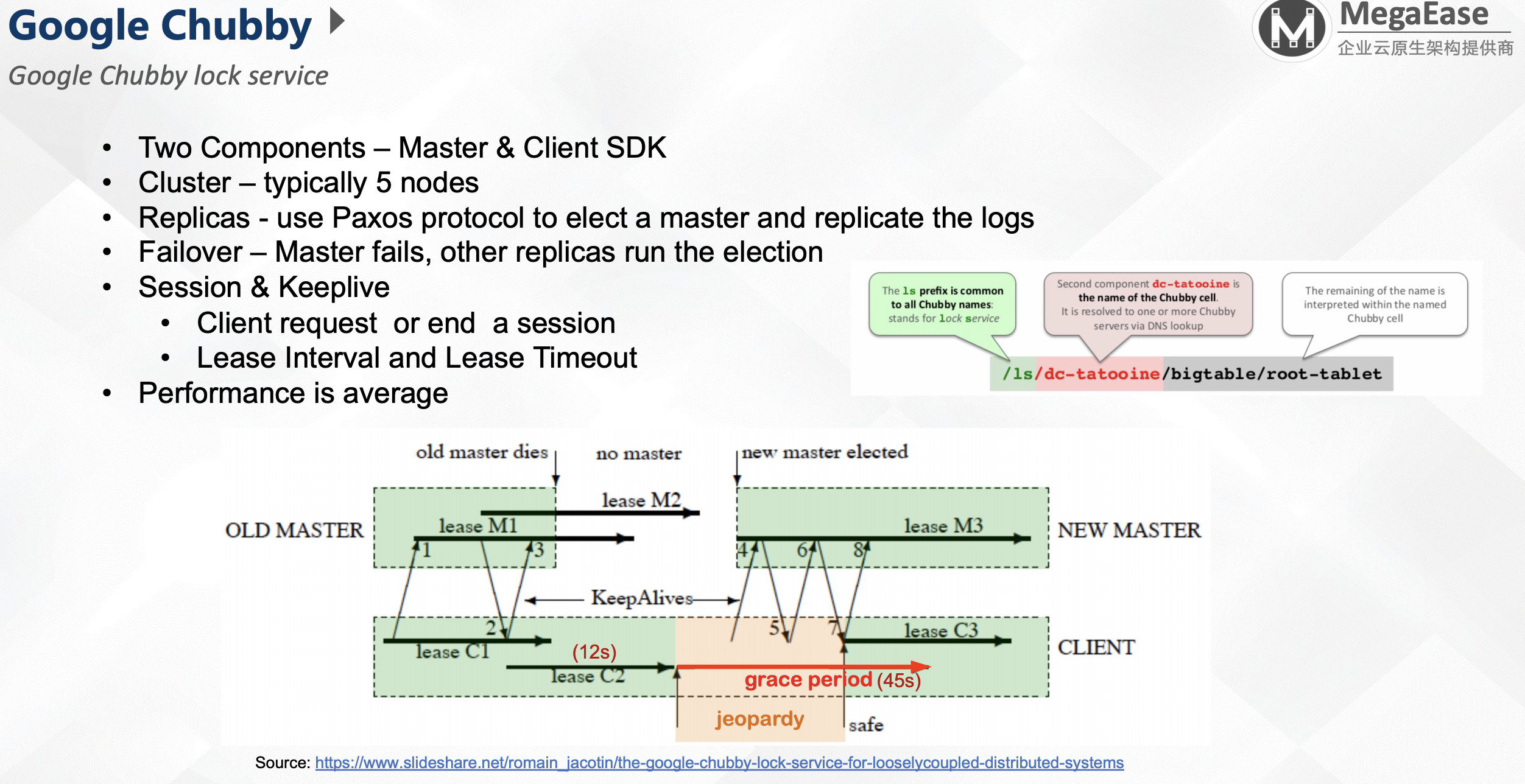
- 两个组件:Master & Client SDK
- 集群:典型的5个节点
- 副本:使用Paxos来选主与副本
- Failover:Master失败后,其他副本进行选举
- Session & Keepalive
- 客户端请求或结束session
- 租约间隔与租约释放
- 性能一般
除了论文,还可看这个进行了解:https://www.slideshare.net/romain_jacotin/the-google-chubby-lock-service-for-looselycoupled-distributed-systems
需要说明,为了防止脑裂,每个master使用不同的周期。每次client连接新的master时,需要协商获取周期。
总结
- Concurrent transaction need be synchronized
- DB Lock is fine, but the Optimistic Lock is great.
- Sharding the data cannot solve the all of problem
- Distributed Lock Service need the following features:
- High Availability
- Data Replicas - strong consistent protocol – Pasox, Raft, zab
- Master Failover – Leader election
- Deadlock Detection
- Keepalive & Lease Timeout
- High Availability